Kauai Physical Therapy Blog
Home of Action Physical Therapy: Kauai's Premier Physical Therapy and Personal Fitness Clinic
Spine
Greenback Therapy; Starting with PT for Back Pain Equals Bigger Cost Savings
When new patients suffering lower back pain begin their treatment with physical therapy, they spend less and accrue fewer medical costs associated with their condition. Those are the findings posted in a recent study in the scientific journal Health Services Research.
 Researchers found that patients who were referred to physical therapy compared to those who were referred for MRI (Magnet Resonance Imaging) for lower back pain paid almost a third of the costs. Initial referral for physical therapy cost $504 on average (for an average 3.8 visits), compared with an average of $1,306 for MRI. Subsequent costs over the next year also came in less—nearly 72% lower for patients who began with a physical therapy referral.
Researchers found that patients who were referred to physical therapy compared to those who were referred for MRI (Magnet Resonance Imaging) for lower back pain paid almost a third of the costs. Initial referral for physical therapy cost $504 on average (for an average 3.8 visits), compared with an average of $1,306 for MRI. Subsequent costs over the next year also came in less—nearly 72% lower for patients who began with a physical therapy referral.
The study also discovered that patients who receive imaging as a first referral increased the likelihood of surgery and injections as well as specialist and emergency department visits within a year. “This is one of many studies demonstrating that physical therapy is a cost-effective alternative to medication and surgery,” said American Physical Therapy Association President Paul Rockar Jr, PT, DPT, MS. “Patients benefit from an active approach to their care and, in turn, society is transformed through the benefits from reduced financial burdens on our health care system.”
Amputee controls two prosthetic limbs by thinking. Wait, what?
Les Baugh was able to use prosthetic arms by simply thinking about it.
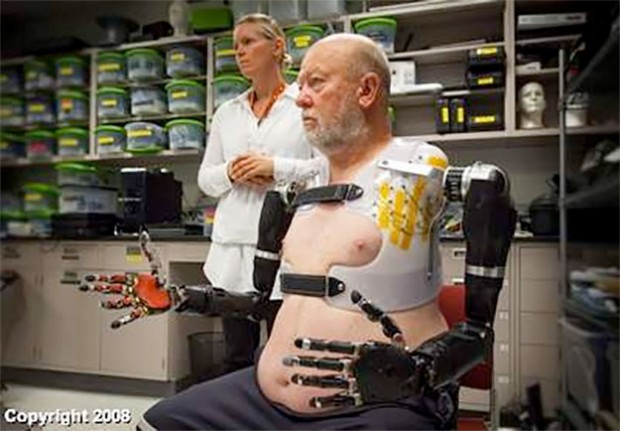 A Colorado man became the first bilateral shoulder-level amputee to wear and simultaneously control two of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Modular Prosthetic Limbs (MPL). Les Baugh was able to operate the system by simply thinking about moving his limbs.
A Colorado man became the first bilateral shoulder-level amputee to wear and simultaneously control two of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Modular Prosthetic Limbs (MPL). Les Baugh was able to operate the system by simply thinking about moving his limbs.
Before testing the limb system, Baugh underwent a surgery known as targeted muscle reinnervation. “It’s a relatively new surgical procedure that reassigns nerves that once controlled the arm and the hand,” John Hopkins trauma surgeon Albert Chi, MD, said in a release.
Then Baugh was fitted for a custom socket that supports the prosthetic limbs and also makes the neurological connections. By the time the socket was finished, Baugh said he was more than ready to get started. When he was fitted with the socket and the prosthetic limbs were attached, he moved several objects, including an empty cup from a counter-shelf height to a higher shelf, a task that required him to coordinate the control of eight separate motions.
“What really was amazing – and was another major milestone with MPL control – was his ability to control a combination of motions across both arms at the same time. This was a first for simultaneous bimanual control,” said prosthetist Courtney Moran, MS, CP.
Acetaminophen does NOT effect recovery time in Low Back Pain
Or should that be a question: Acetaminophen does NOT effect recovery time in Low Back Pain?
 Despite being recommended by more than 15 different Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPGs) for Low Back Pain (LBP) Since 1987, it seems as if maybe Tylenol doesn’t help recovery time.
Despite being recommended by more than 15 different Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPGs) for Low Back Pain (LBP) Since 1987, it seems as if maybe Tylenol doesn’t help recovery time.
A large and compelling recent study titled “Efficacy of paracetamol for acute low-back pain: a double blind, randomized controlled trial” recently evaluated the role of paracetamol (acetaminophen) in managing acute LBP.
It found there were NO statistically significant differences between the placebo group or either of the acetaminophen groups for recovery time, adherence to tablet usage, and adverse events.
Chronic Neck Pain
A recent study reveals that an effective exercise regimen and its components regarding frequency, intensity, time and type (FITT) will improve Chronic Neck Pain.

Chronic Neck Pain (CNP) is treated by many therapists with exercise therapy, but what delivers the best results? According to a recent study published by Elsevier Inc. / American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine, the objective was to identify the most effective components in an active exercise physiotherapy treatment intervention for CNP based on the frequency, intensity, time, and type (FITT) exercise method.
The study revealed that education and exercise training has the most beneficial effect on reducing pain and improving function and quality of life in patients with CNP. It was also noted that targeting deep neck flexors through strength training has positive effects on quality of life when combined with endurance and aerobic training. Progress was seen in patients that performed 30-60 minutes exercise sessions at least three times per week for 6-12 weeks.
Click here to view the article posted on www.anatomy-physiotherapy.com’s web site.
How to Reduce Back Pain From Cycling | Play Better | Core Daily | Core Performance
 How to Reduce Back Pain From Cycling
How to Reduce Back Pain From Cycling
via How to Reduce Back Pain From Cycling | Play Better | Core Daily | Core Performance.
Understanding Your Spine
Understanding your spine is the first step to proper spinal health
 The 24 separate bones, or vertebrae, all stacked on top of each other make up the structure known as your spine. Those vertebrae are the main framework that protects the most important spinal cord. There are five sections of the spine:
The 24 separate bones, or vertebrae, all stacked on top of each other make up the structure known as your spine. Those vertebrae are the main framework that protects the most important spinal cord. There are five sections of the spine:
• cervical (top 7 vertebrae)
• thoracic (12 vertebrae)
• lumbar (5 vertebrae)
• sacrum
• coccyx
To perform (hopefully) all of those complex movements that the spine is capable of, between each vertebrae is a disc that essentially works as a cushion to absorb shock of the impact your spine endures during both normal activity such as walking, or high stress activity like surfing. And holding the vertebrae and discs together are the ligaments. And completing the spinal structure are the tendons that attach the muscles to the spine itself.
The Sections of the Spine
The cervical spine, the neck, consists of the top seven vertebrae. The cervical spine is the most flexible, complex and mobile region of the spine and enables you to move your head from side to side and up and down. In the cervical spine are two very unique vertebra, the atlas and the axis. It is these vertebrae that are specially adapted to enable such complicated rotation.
The thoracic spine are the 12 vertebrae below the cervical spine section of the spine. Your ribs connect to the vertebrae in the thoracic spine.
The lumbar spine or ‘lower back’ consists of five vertebrae. Sometimes however, there is a sixth vertebrae in the lumbar section of the spine.The lumbar is located below the thoracic section of the spine. The lower back bears a great deal of the weight of the body and for that reason is particularly vulnerable to back pain.


